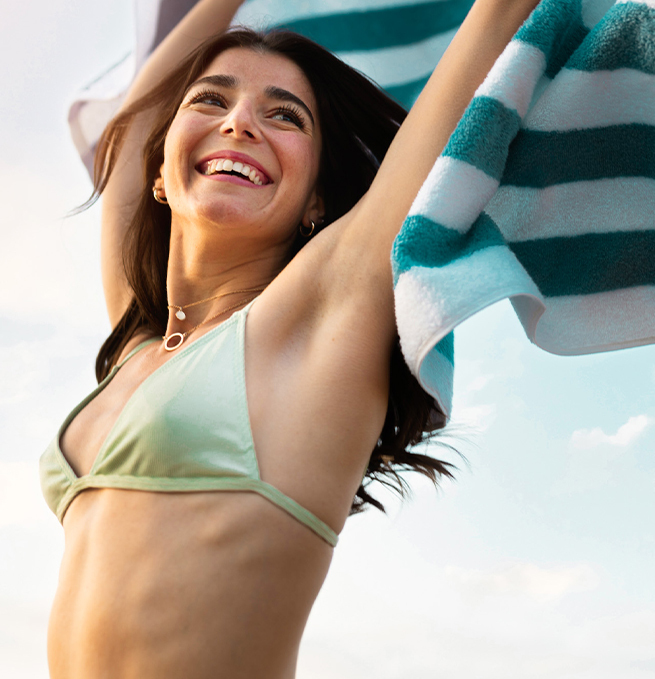
Glowing Skin Awaits: Discover Custom Dermatology

Meet our Doctors
Dr. Orly Cheirif
View profileDr. Nicole Kresch
View profileLive the Bellphoria experience
We can identify the problem and give the solution
At Bellphoria, we understand that your skin is a fundamental aspect of your overall well-being. Our team of highly qualified dermatologists is here to help you identify and address any concerns you may be facing. From common conditions like acne to more specialized issues, we are committed to providing personalized care that highlights the health and beauty of your skin.
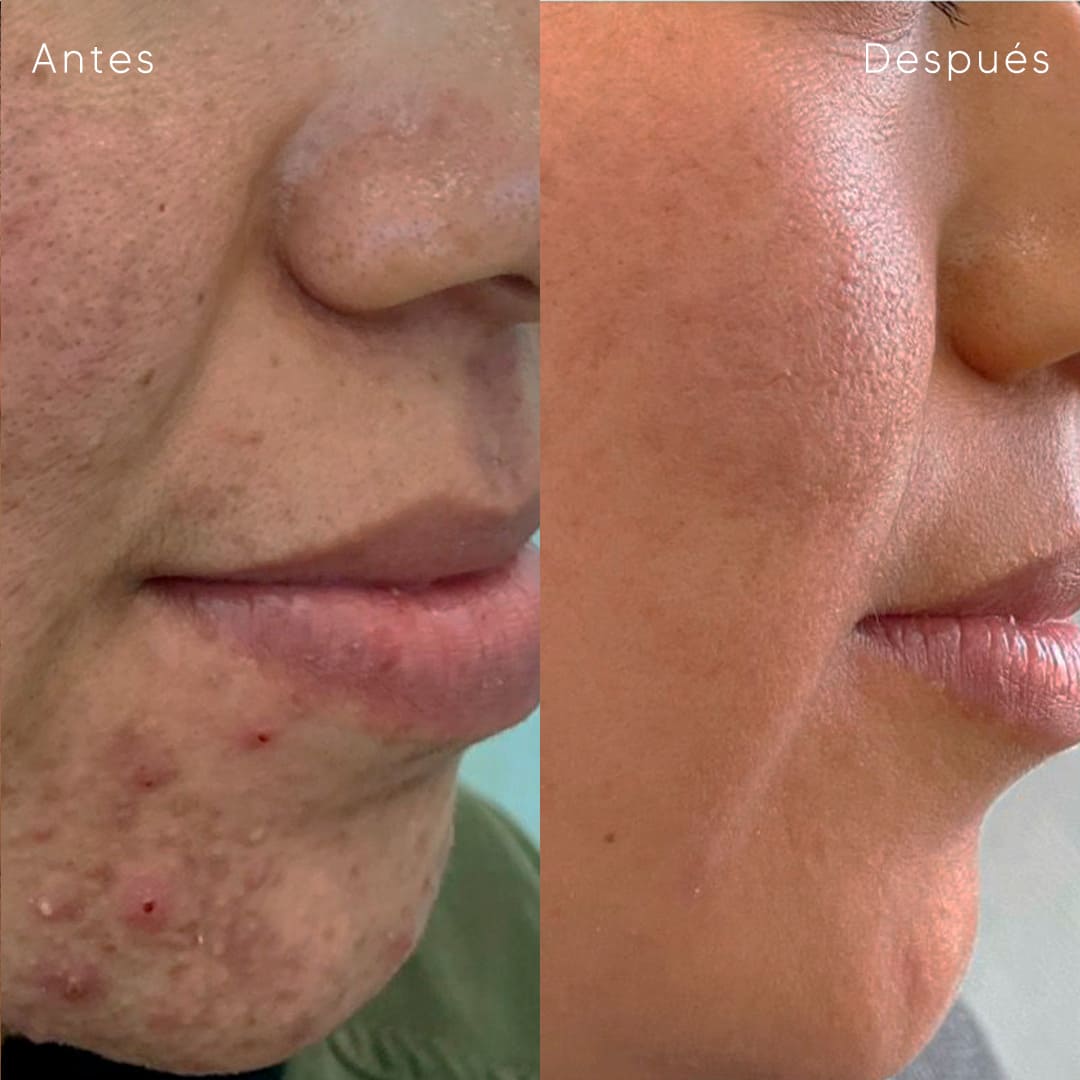
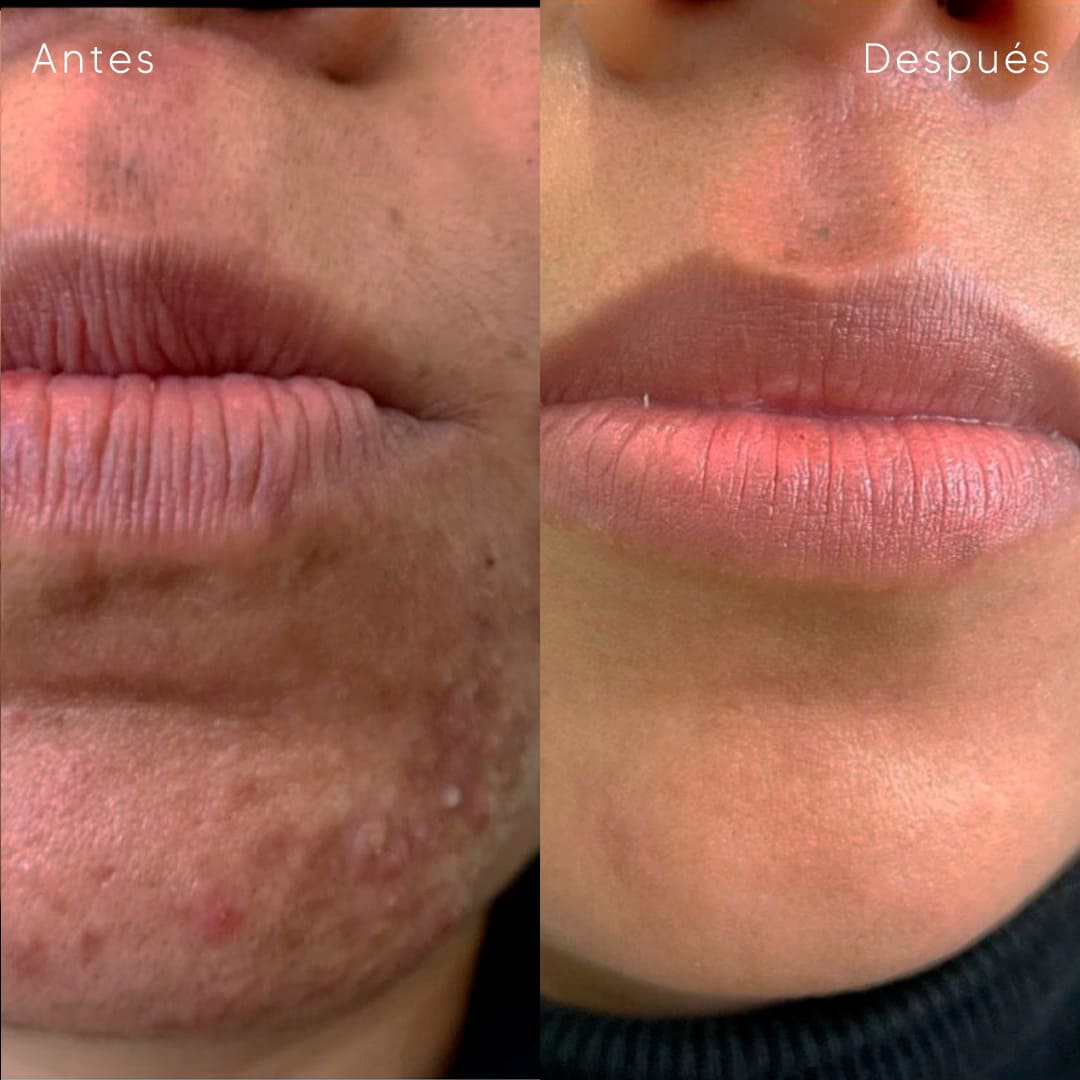
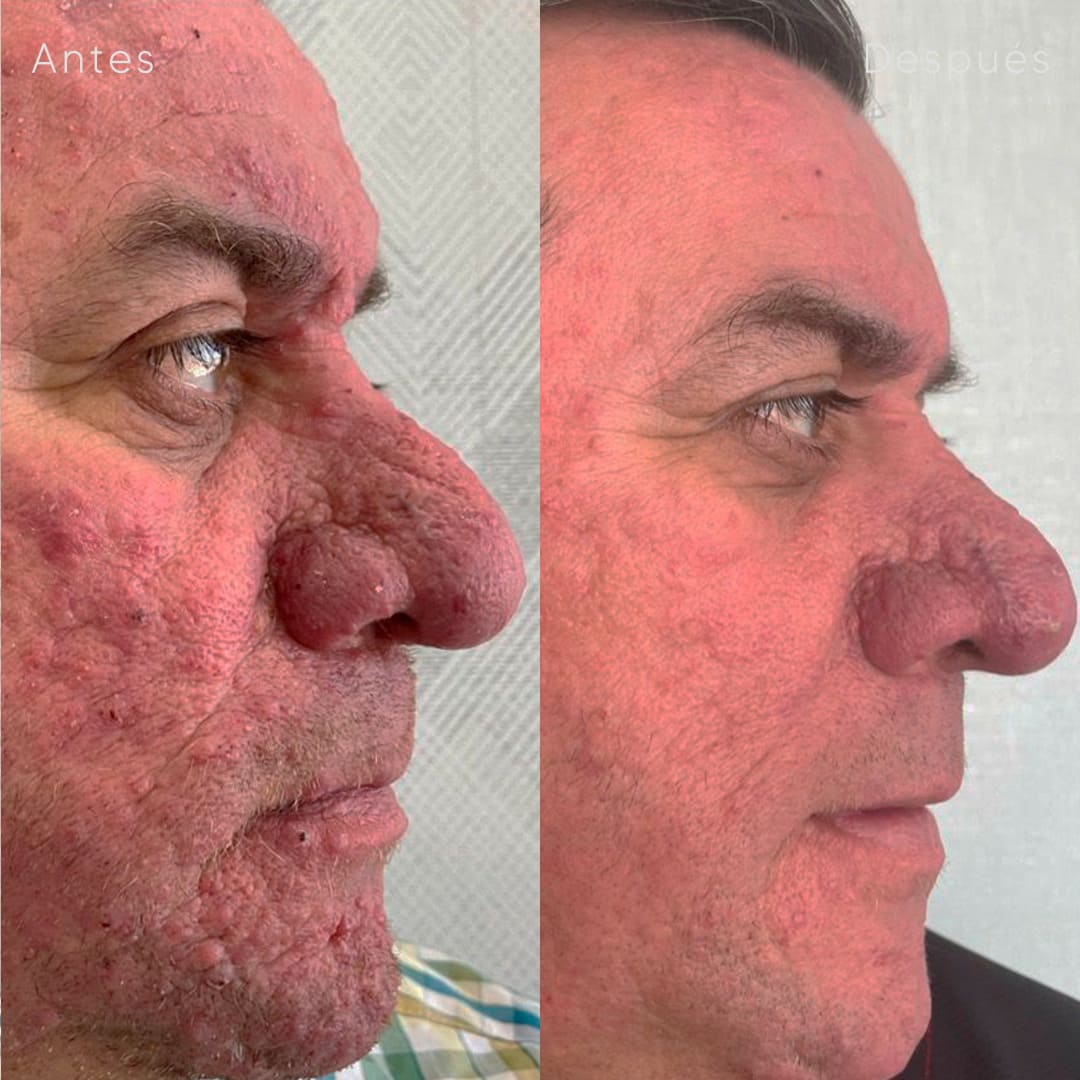
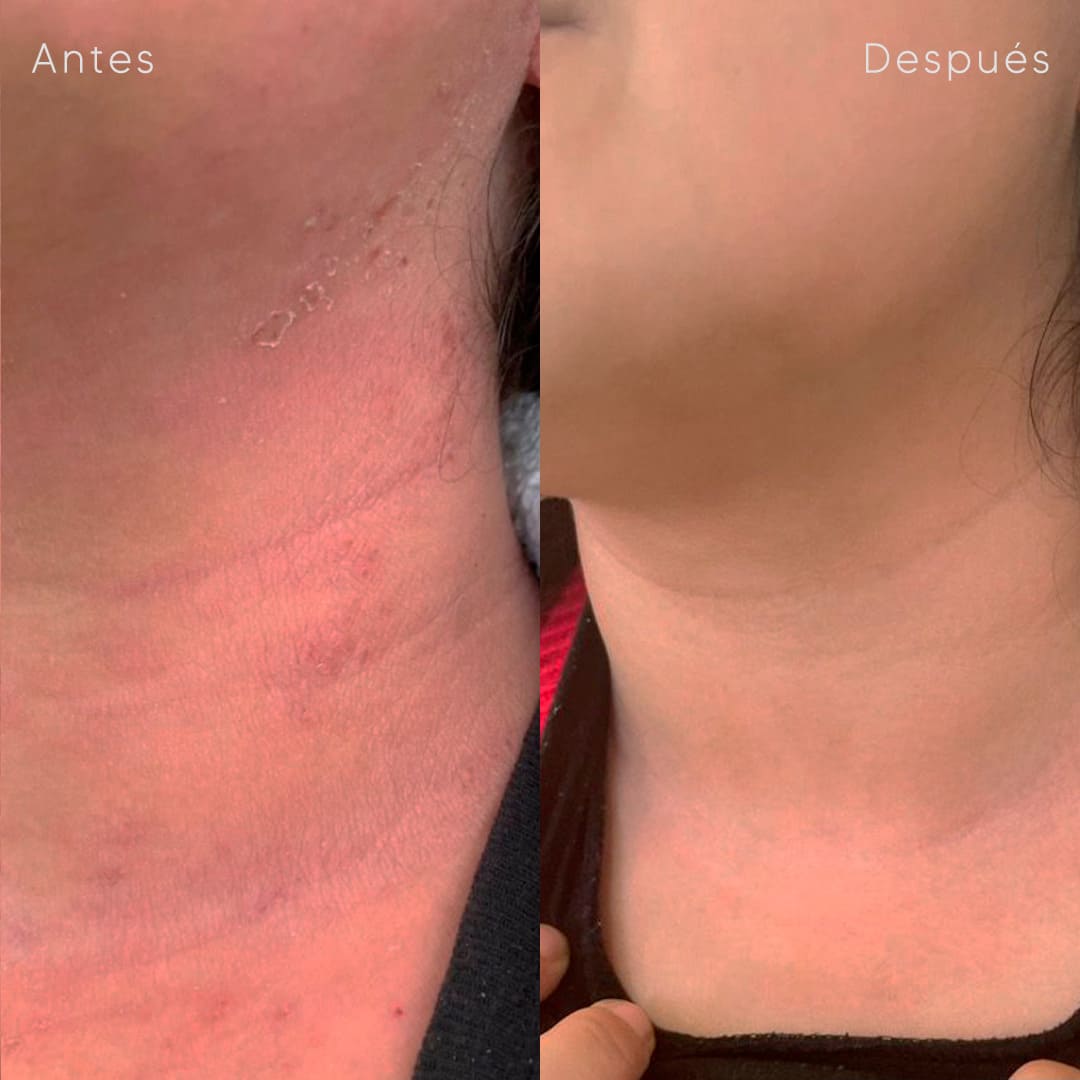
Discover our services for tailored skin solutions—diagnosis, treatment, and advanced care crafted to meet your unique dermatological needs.
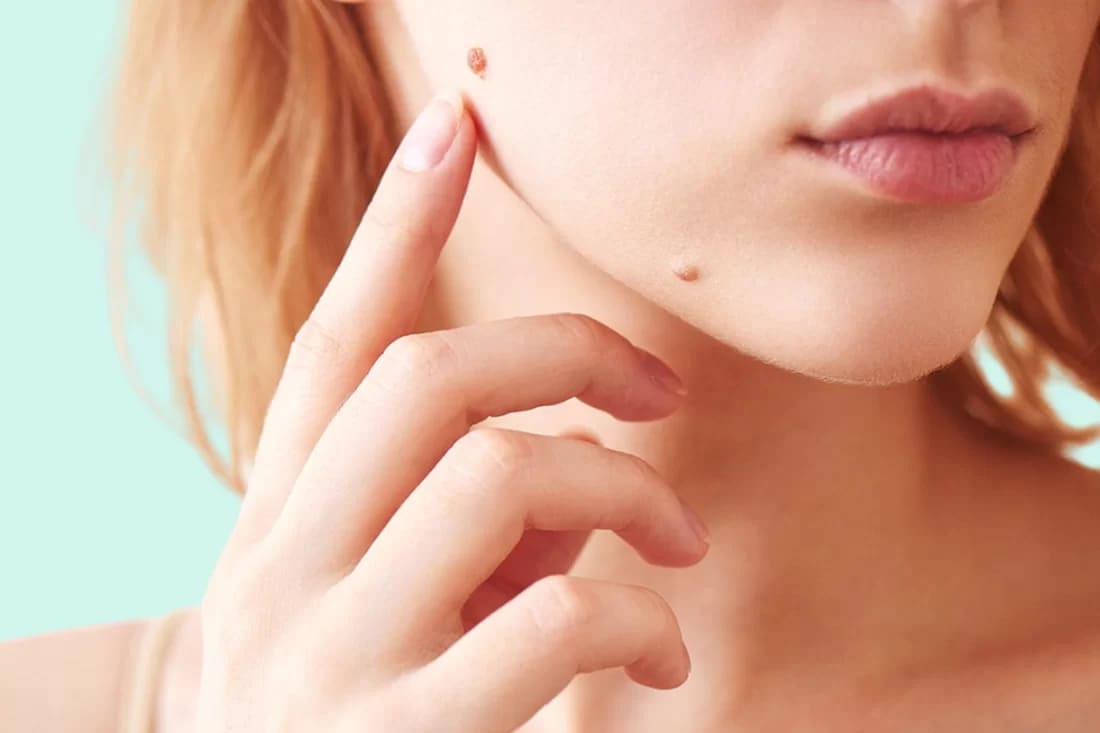

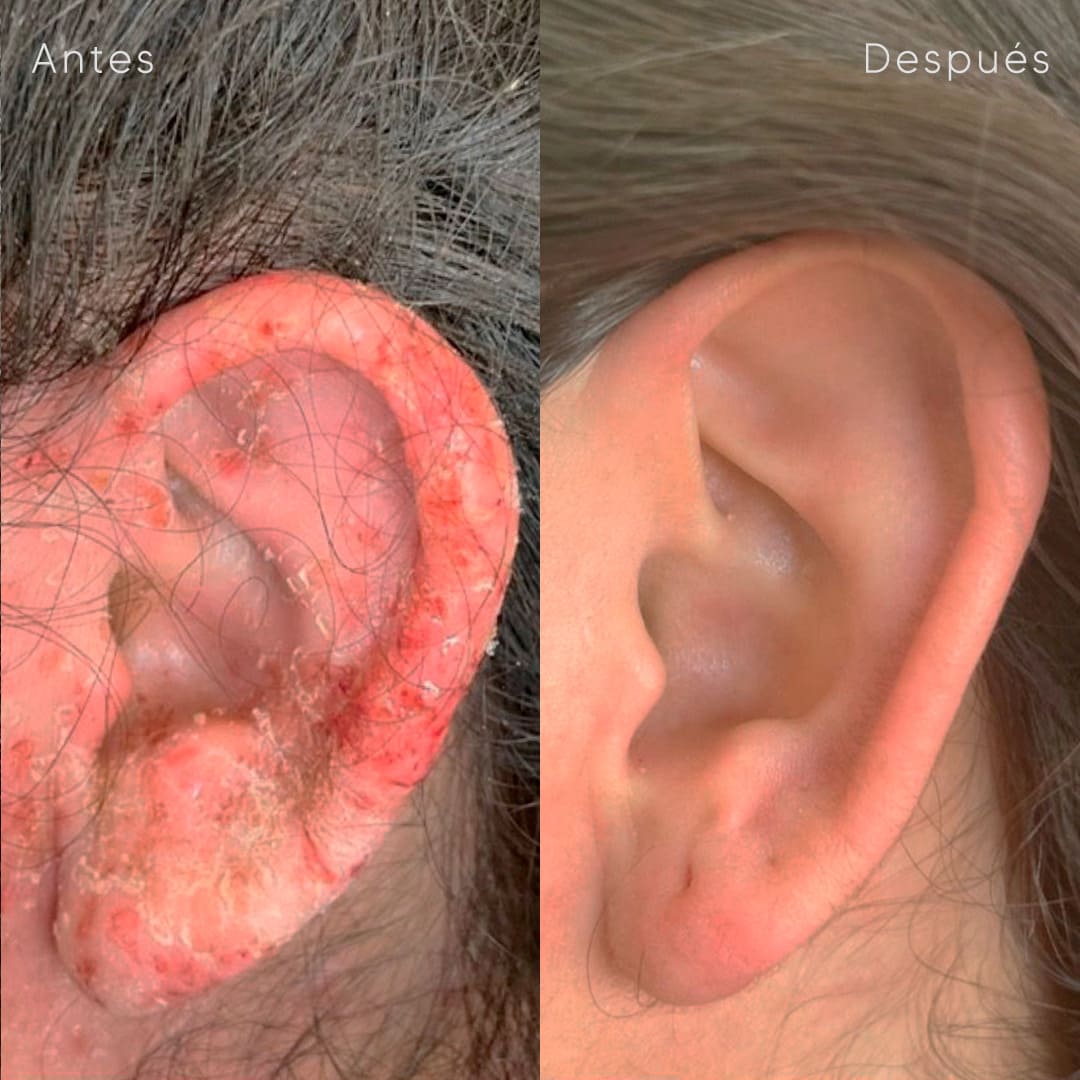
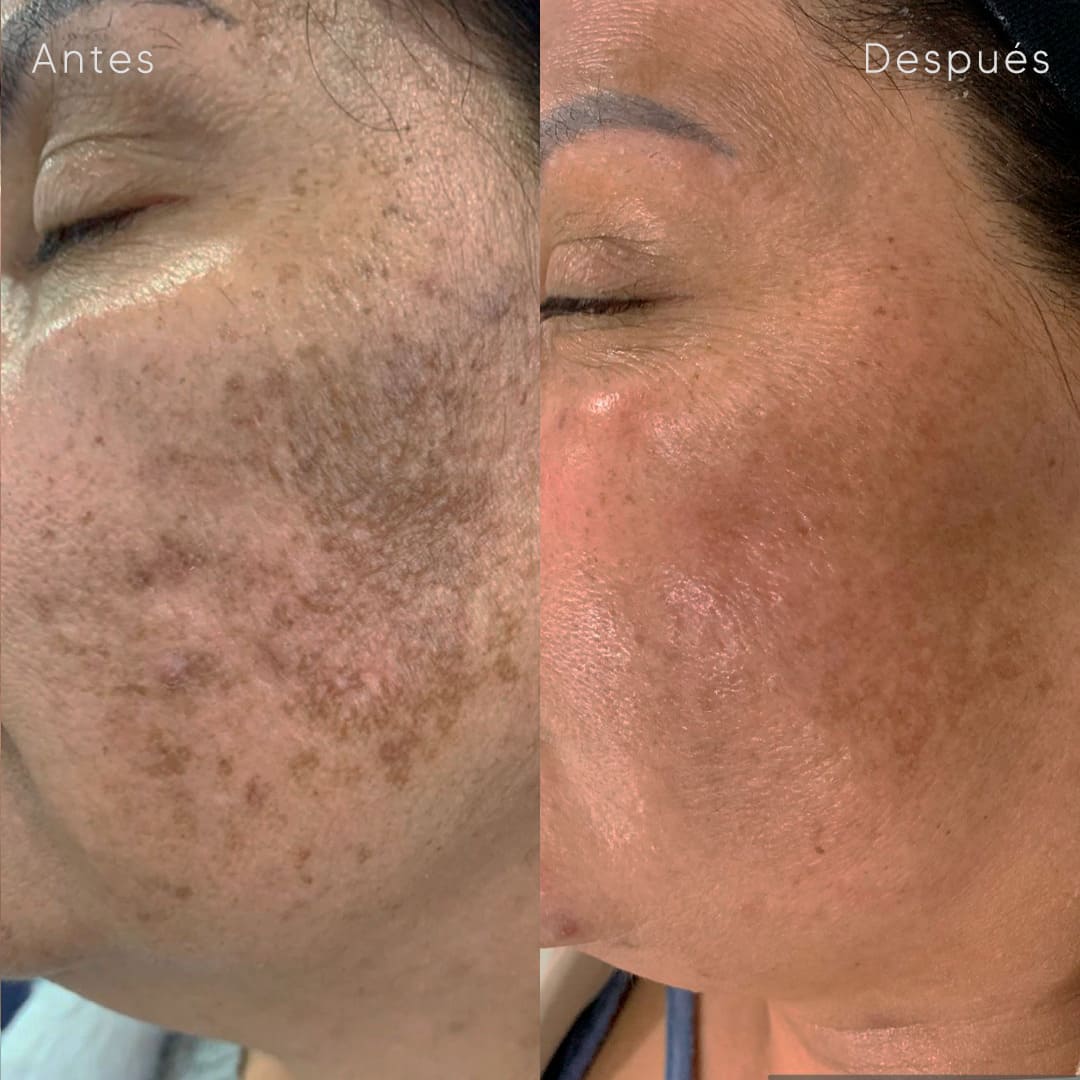
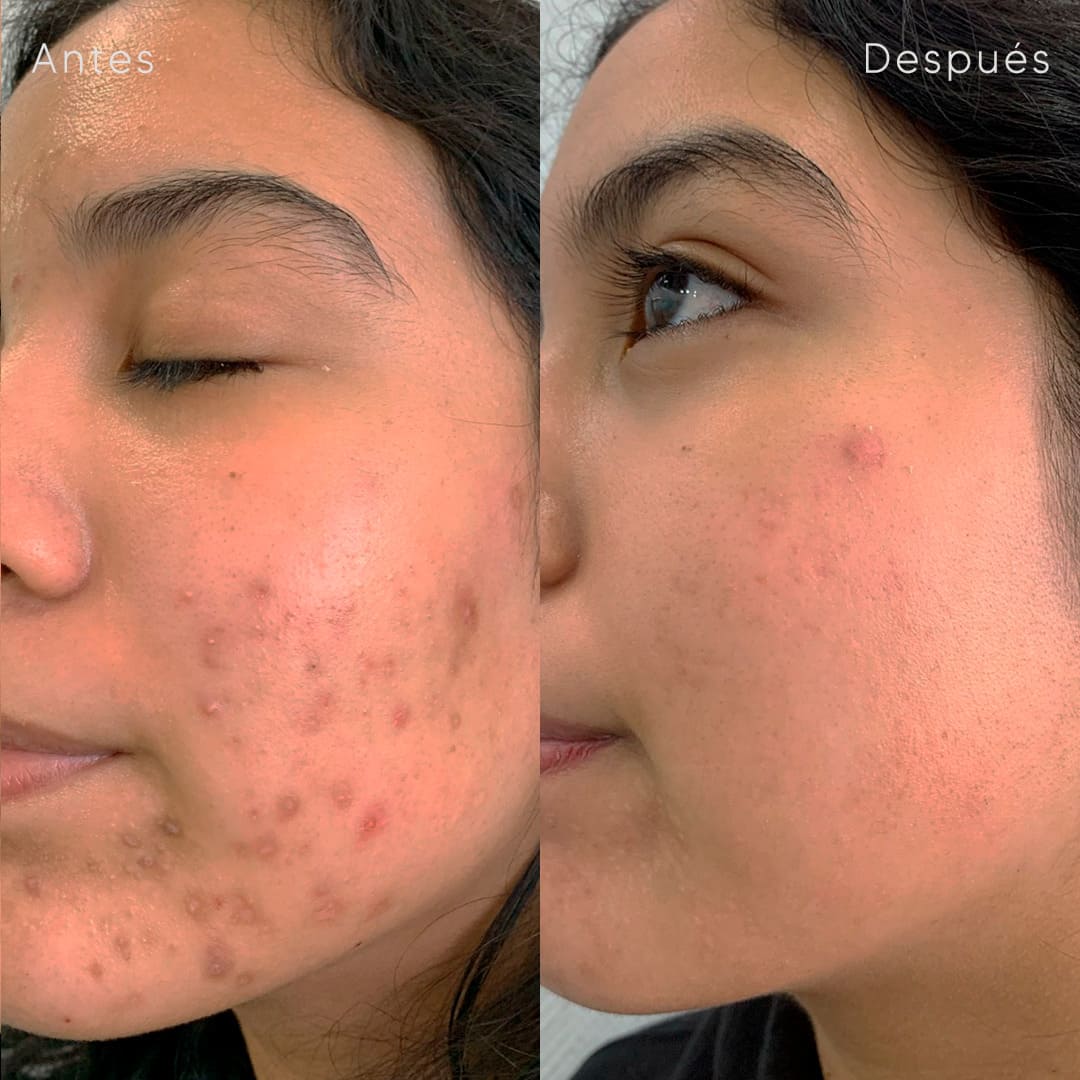
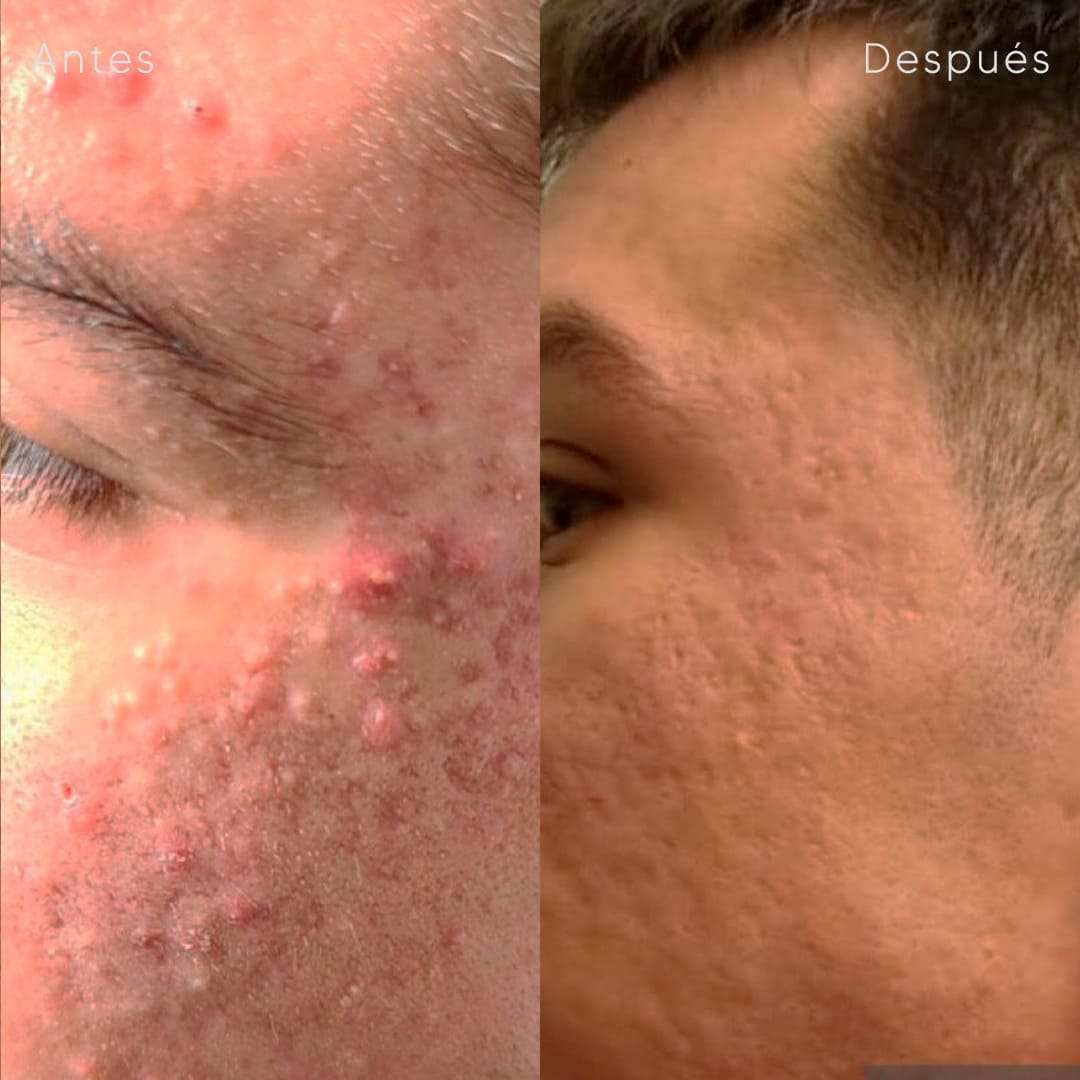
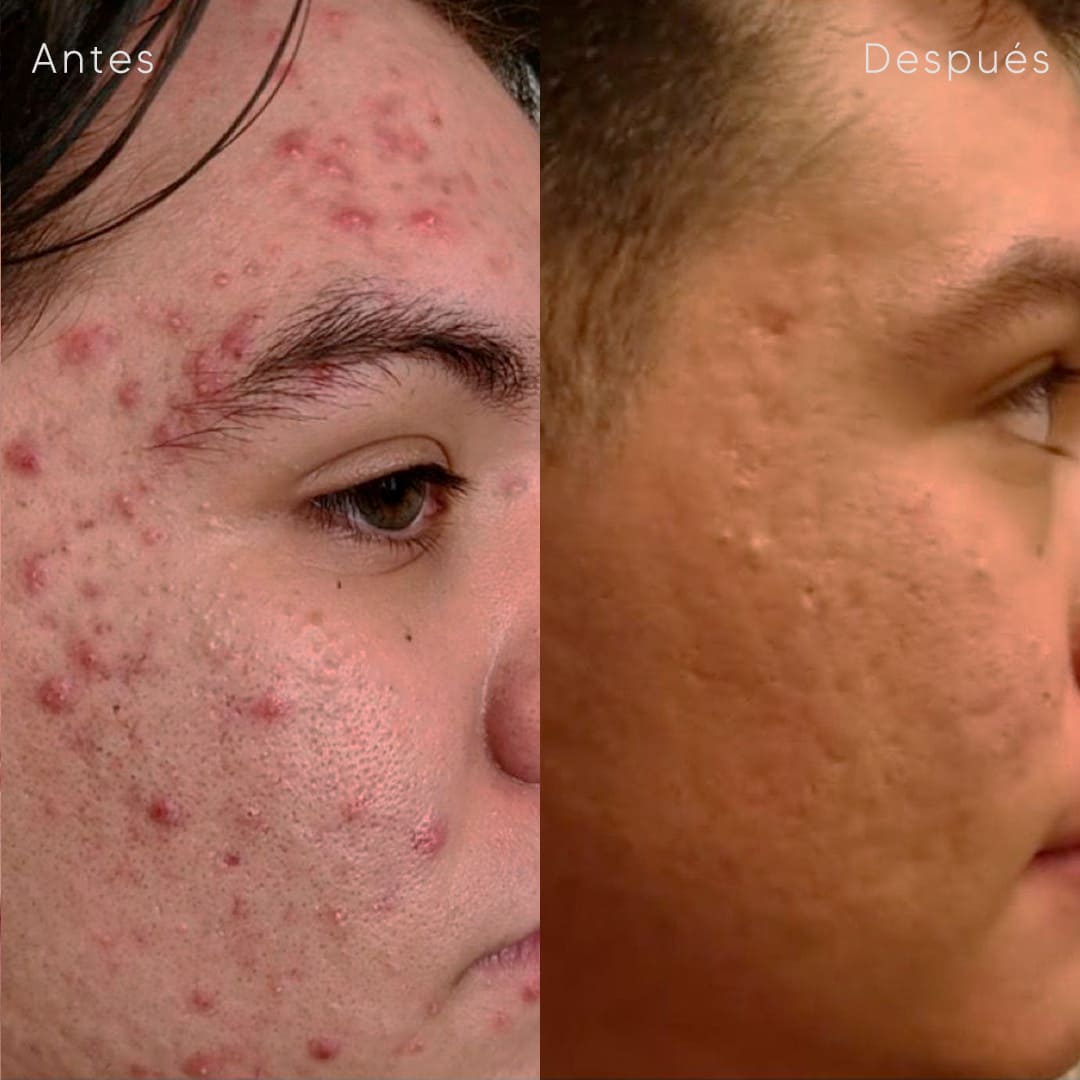
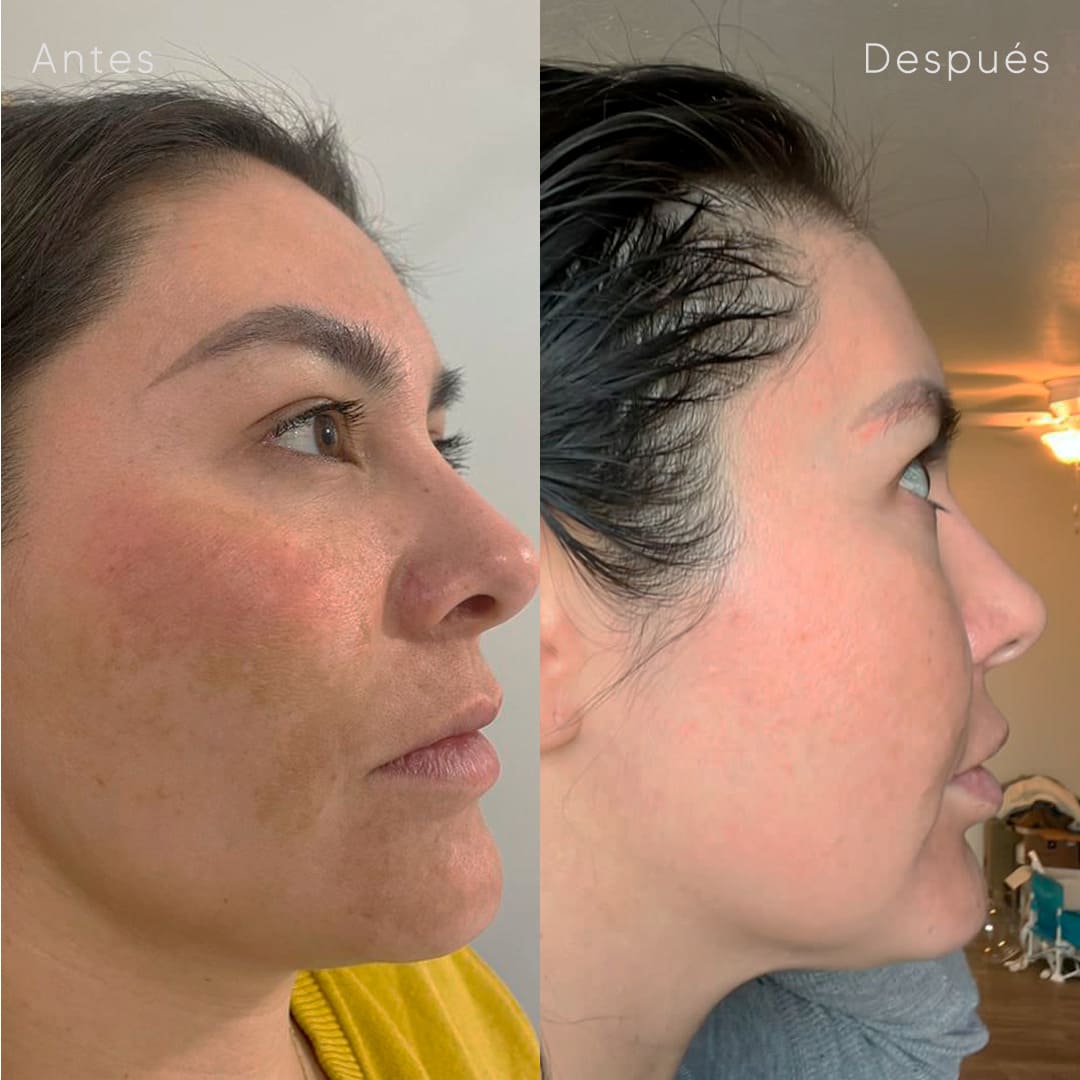

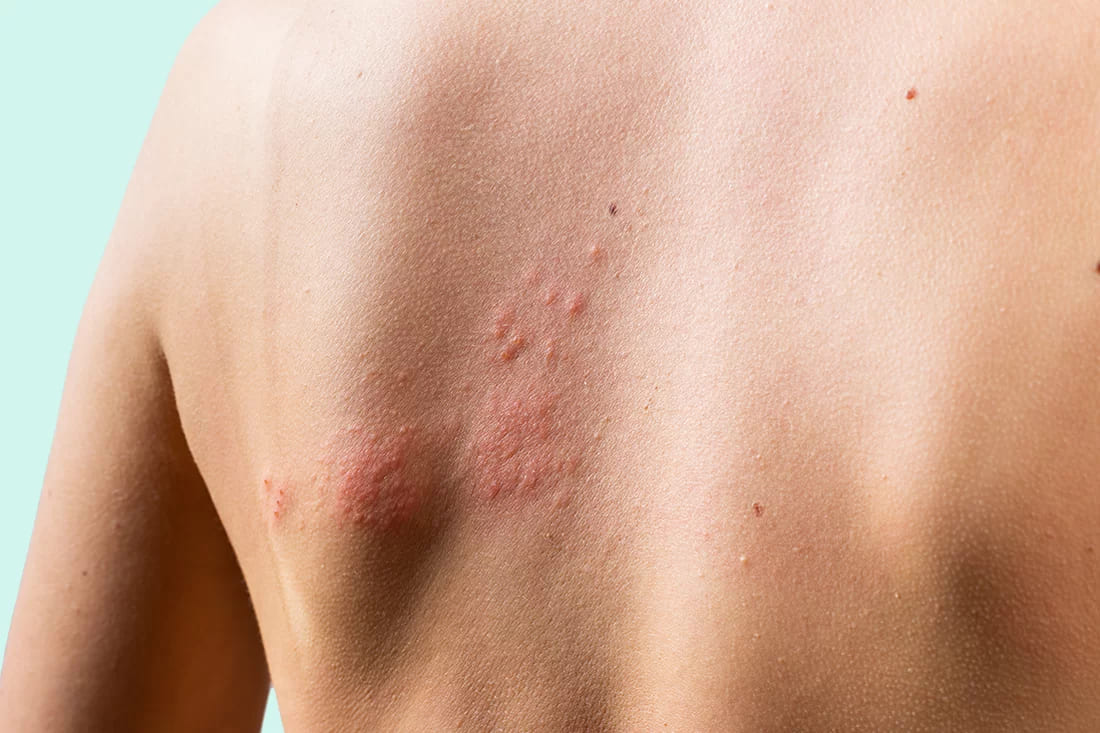





Cysts removal
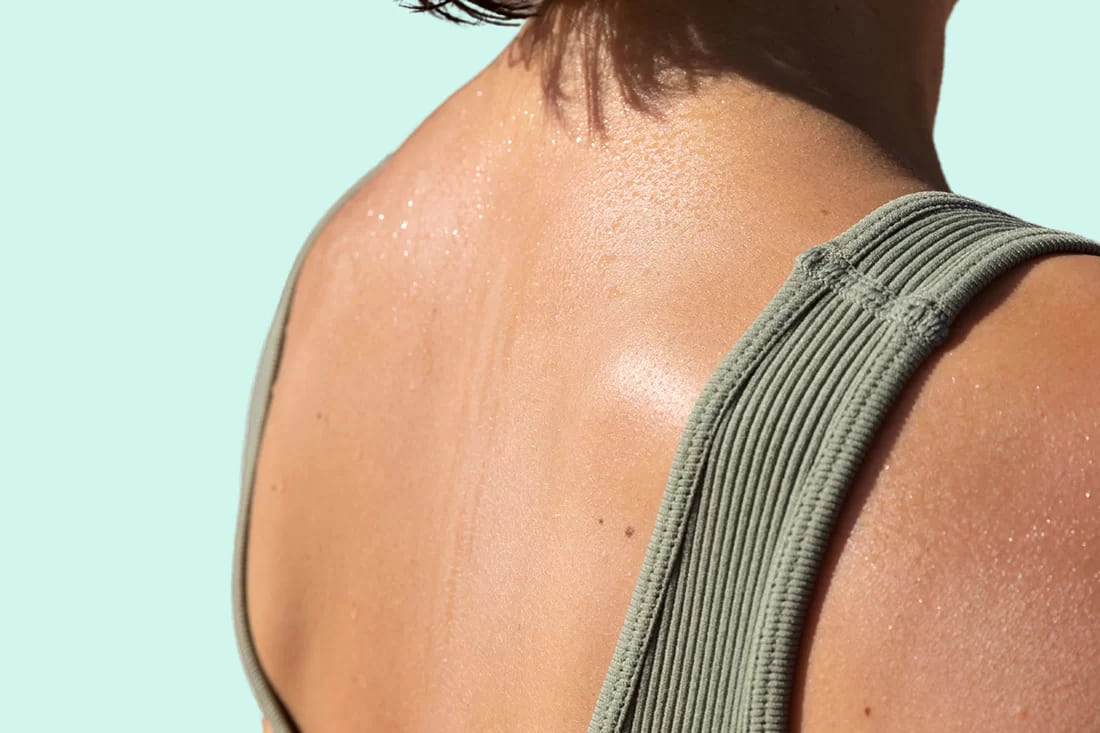

Sweating
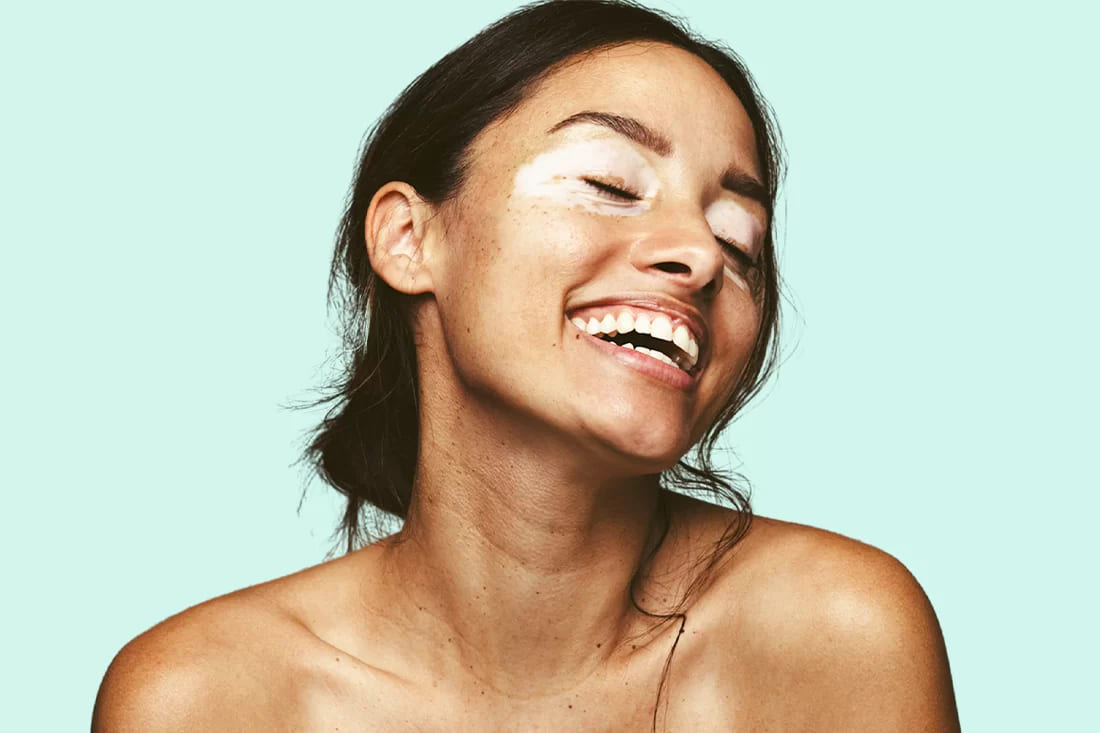
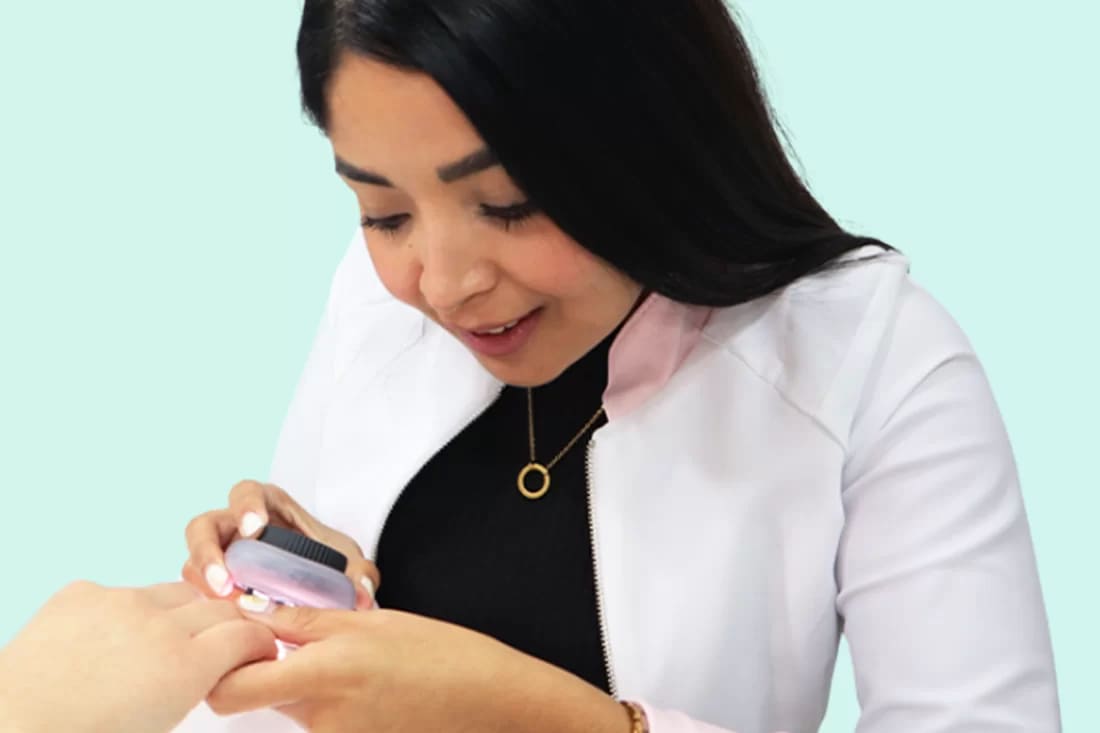



We can identify the problem
and give the solution
At Bellphoria, we understand that your skin is a fundamental aspect of your overall well-being. Our team of highly qualified dermatologists is here to help you identify and address any concerns you may be facing. From common conditions like acne to more specialized issues, we are committed to providing personalized care that highlights the health and beauty of your skin.
Some of the solutions can be
made with our Technology
Acne
Cellulite
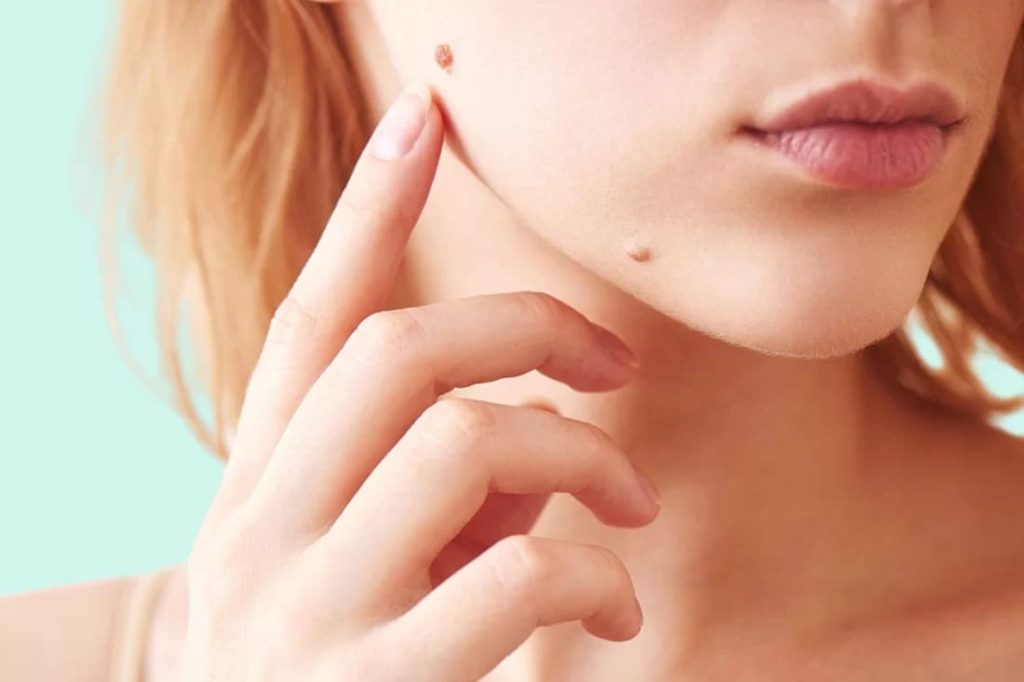
Mole Removal
Scar
Skin lessons
Discover our services for tailored skin solutions—diagnosis, treatment, and advanced care crafted to meet your unique dermatological needs.
Most common diseases
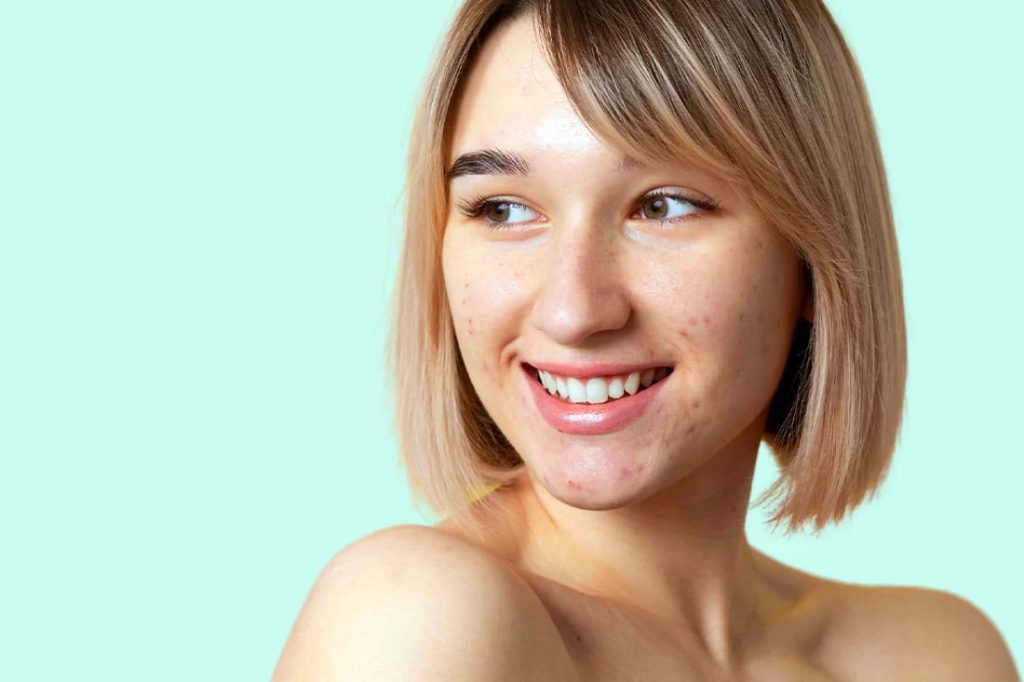

Acne
Dermatitis
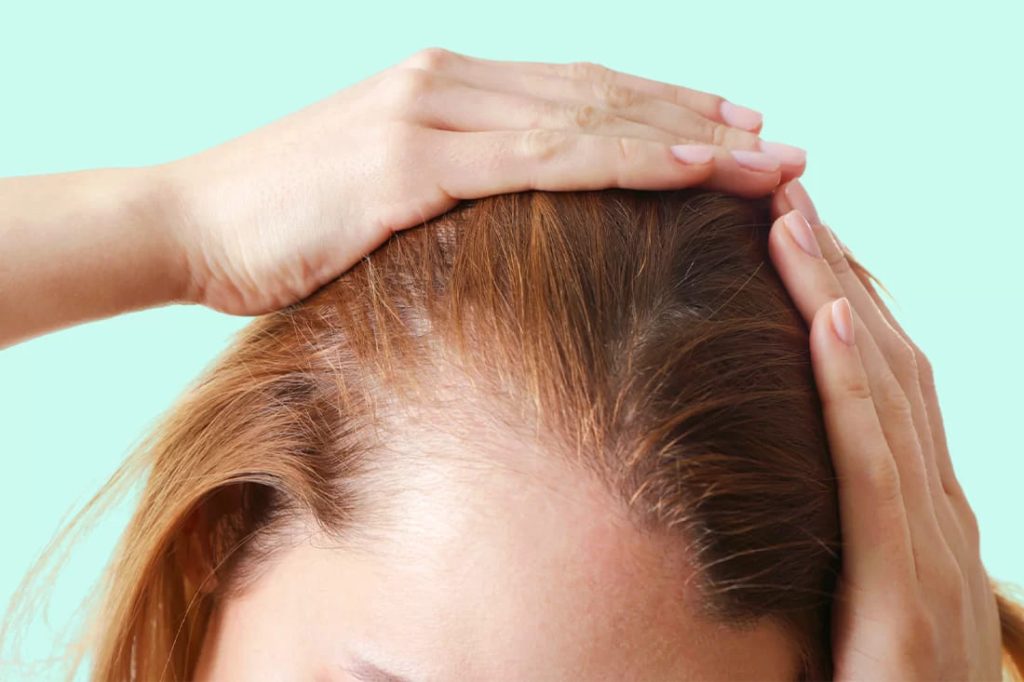

Hair Loss
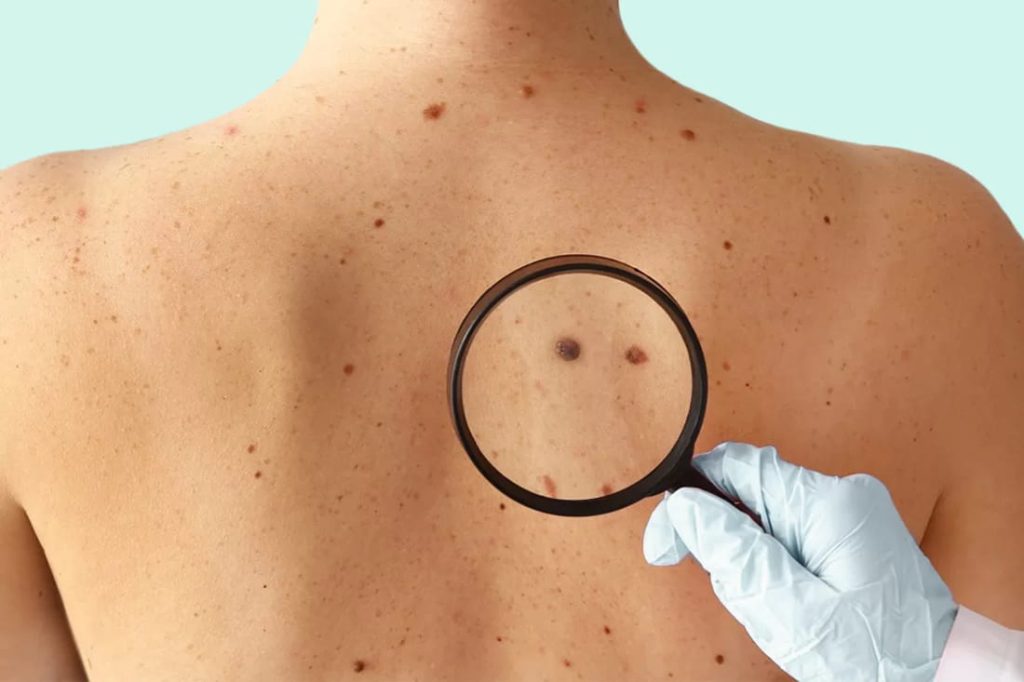
Skin Cancer
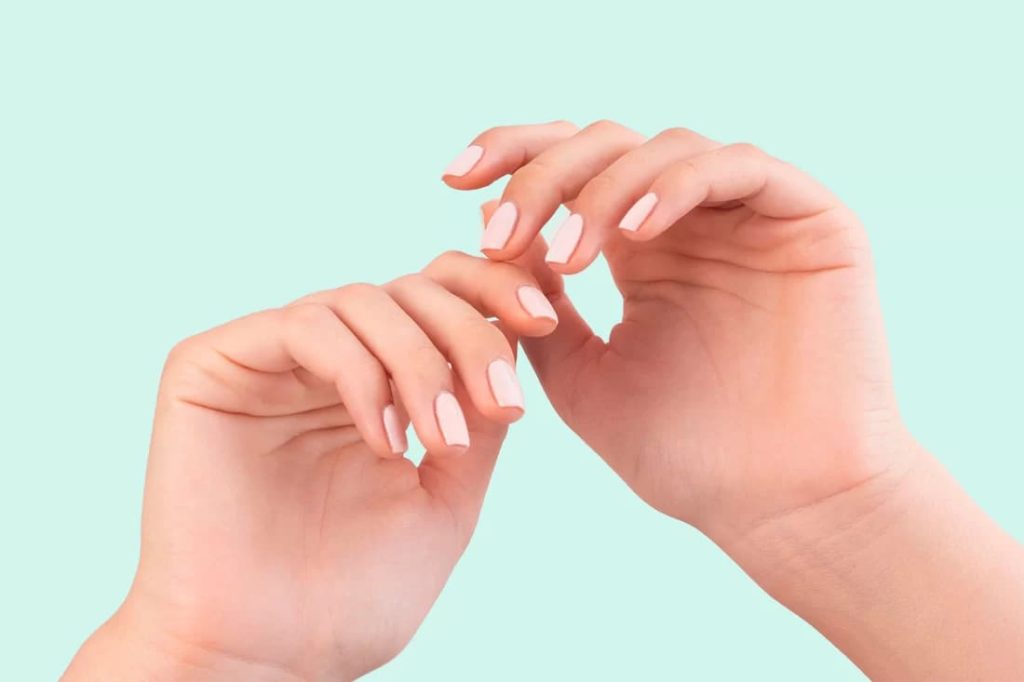

Nail Diseases

Photoaging
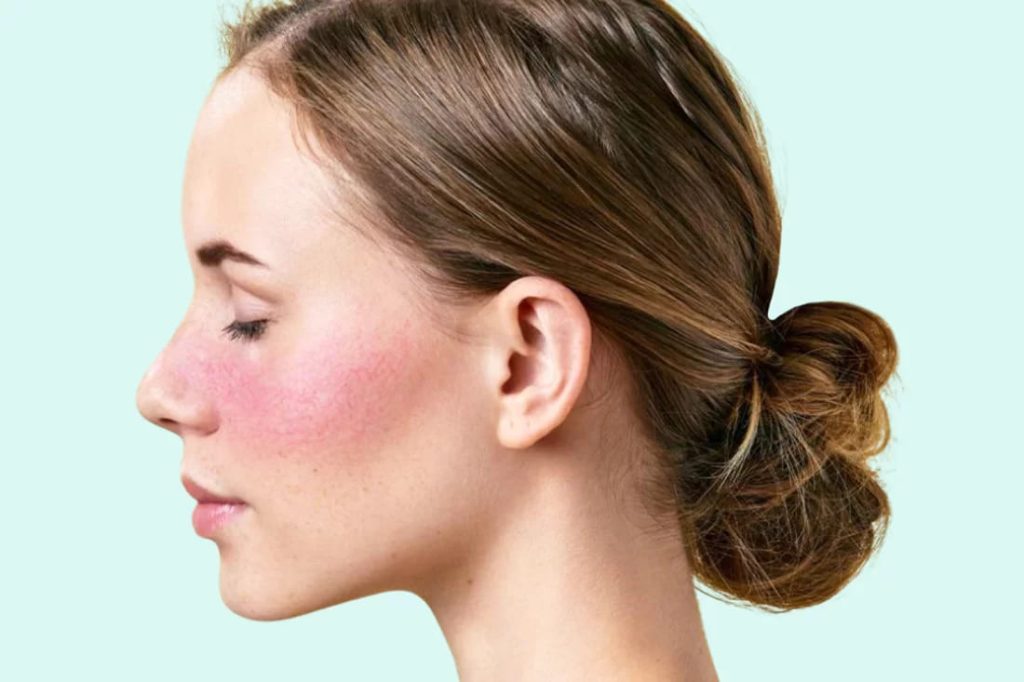

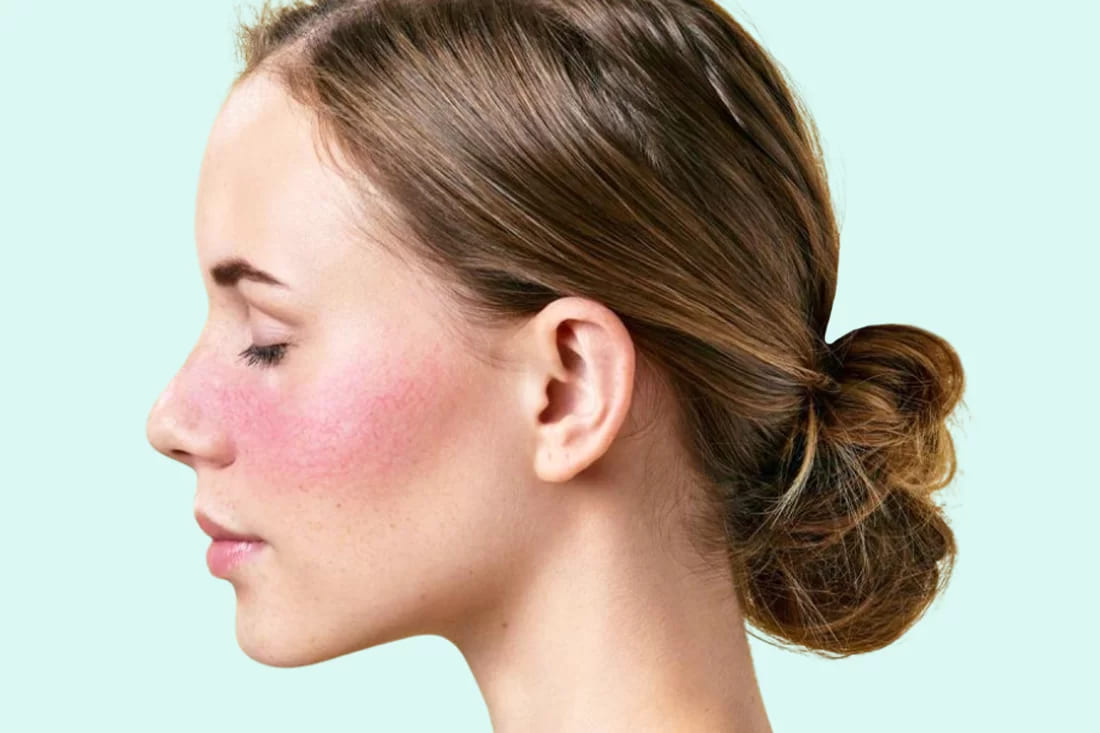
Rosacea
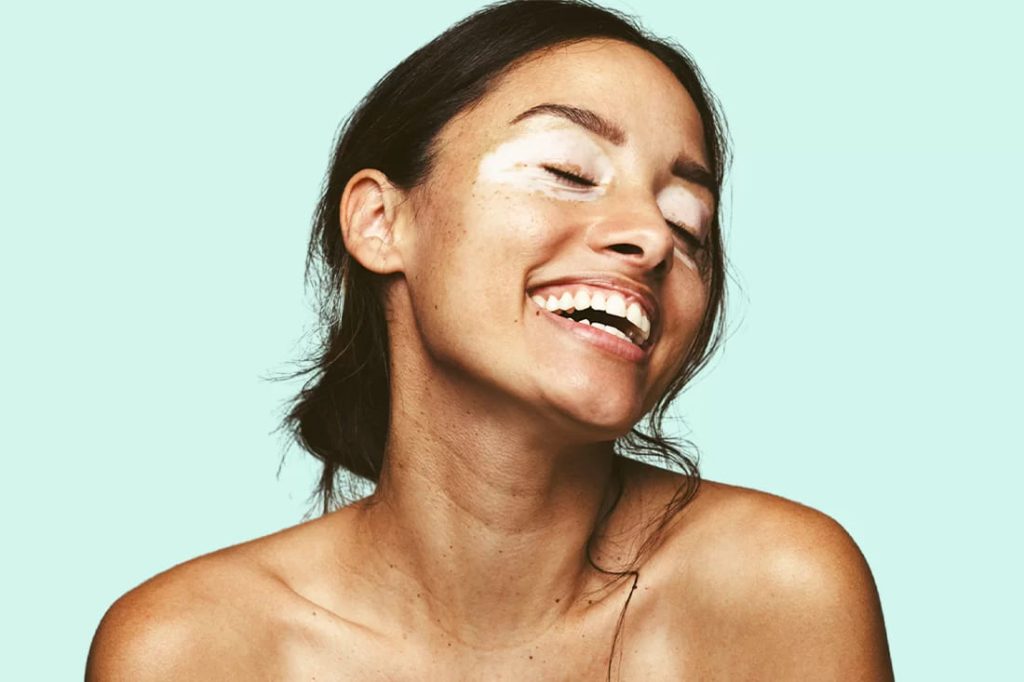

Vitiligo
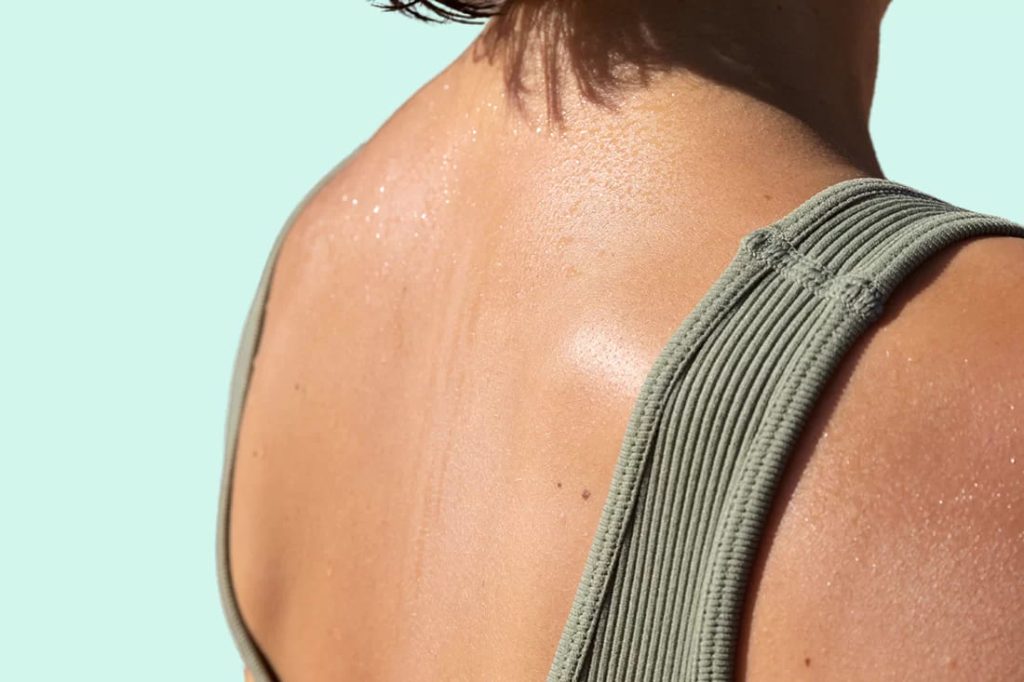

Excessive Sweating
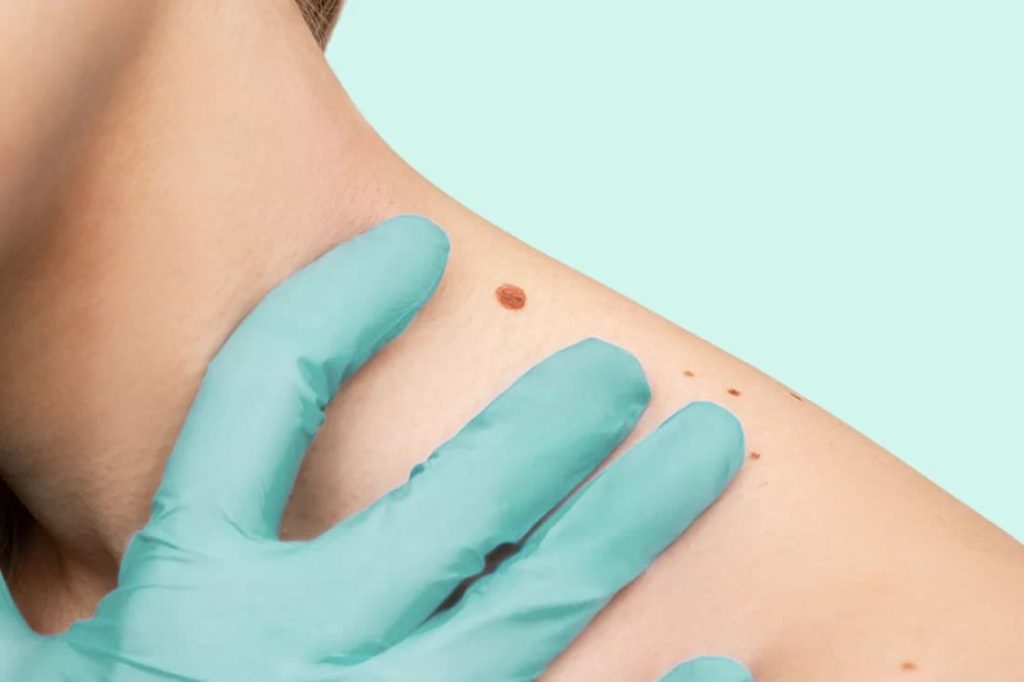
Mole Removal

Wart Removal
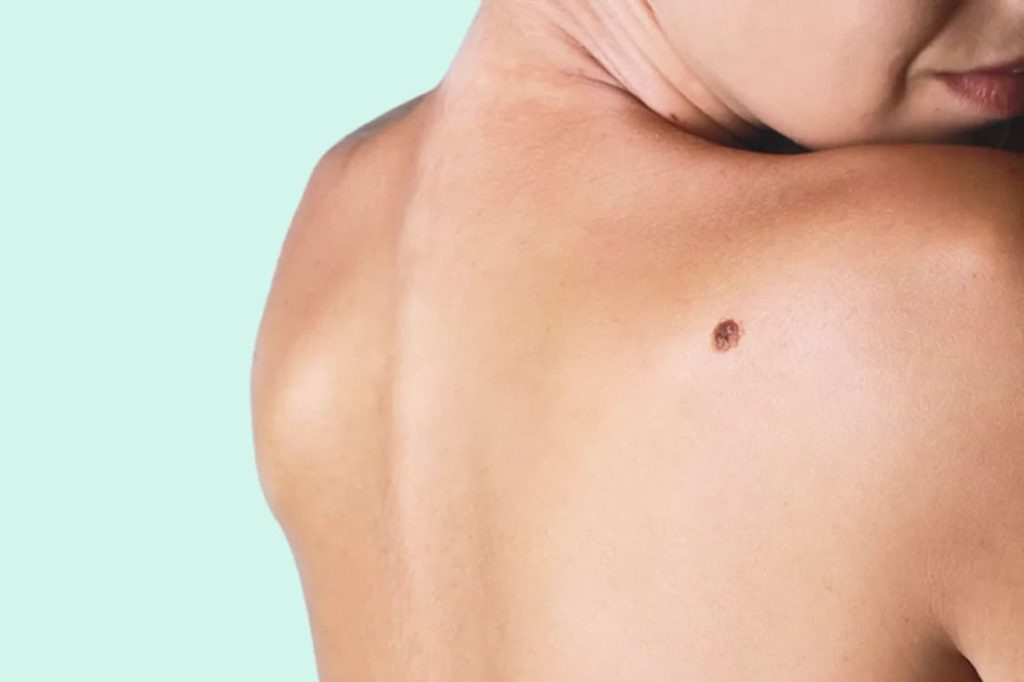
Skin Lesions
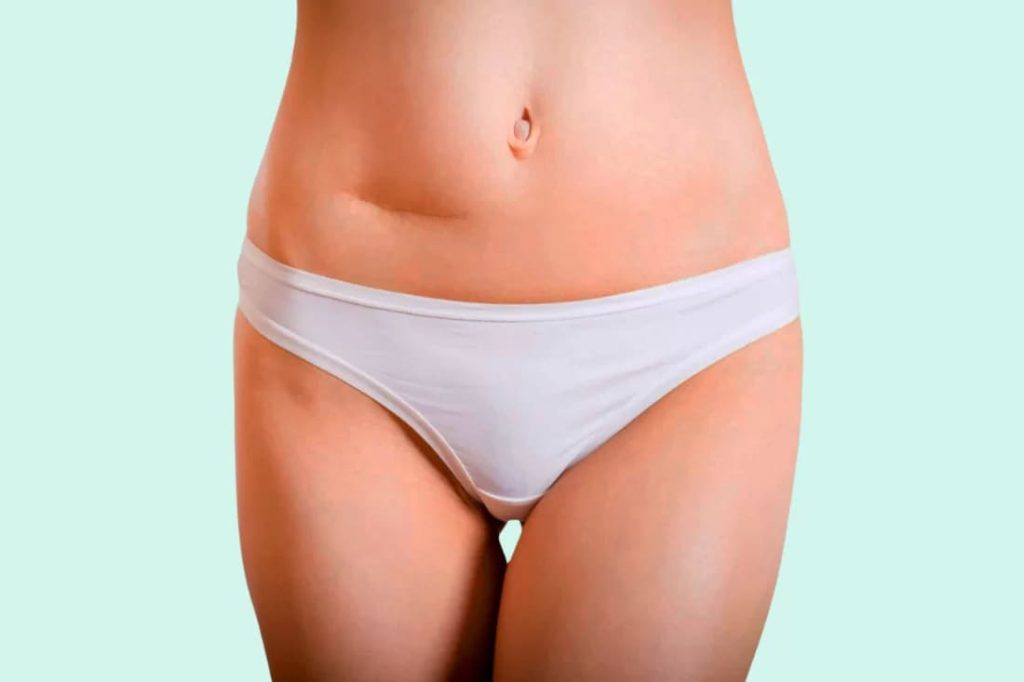
Scar Revision
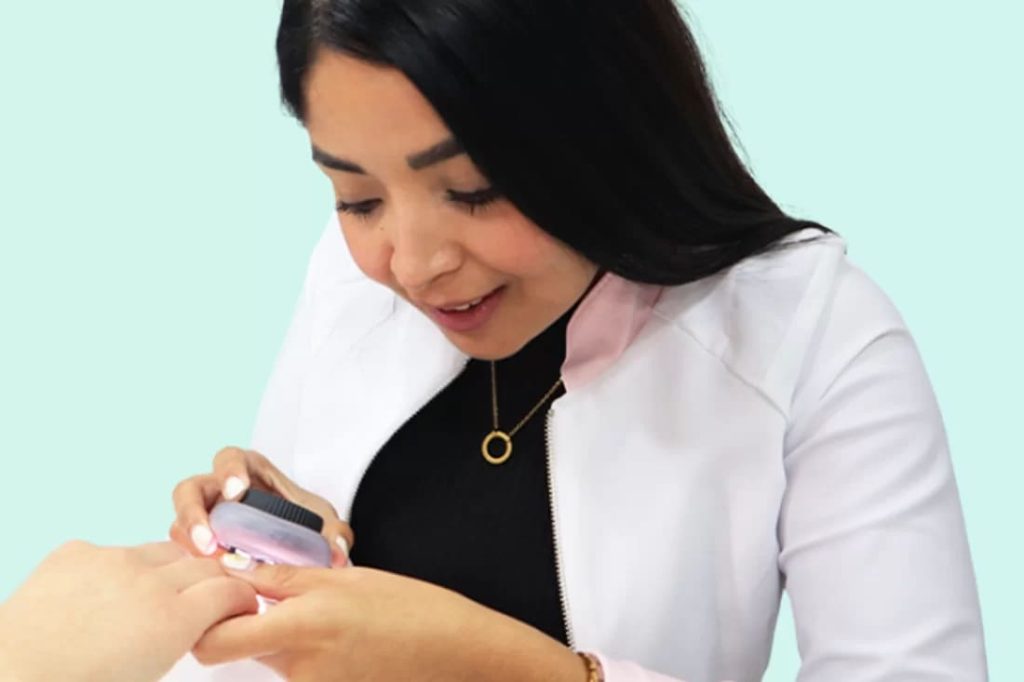

Skin Biopsy
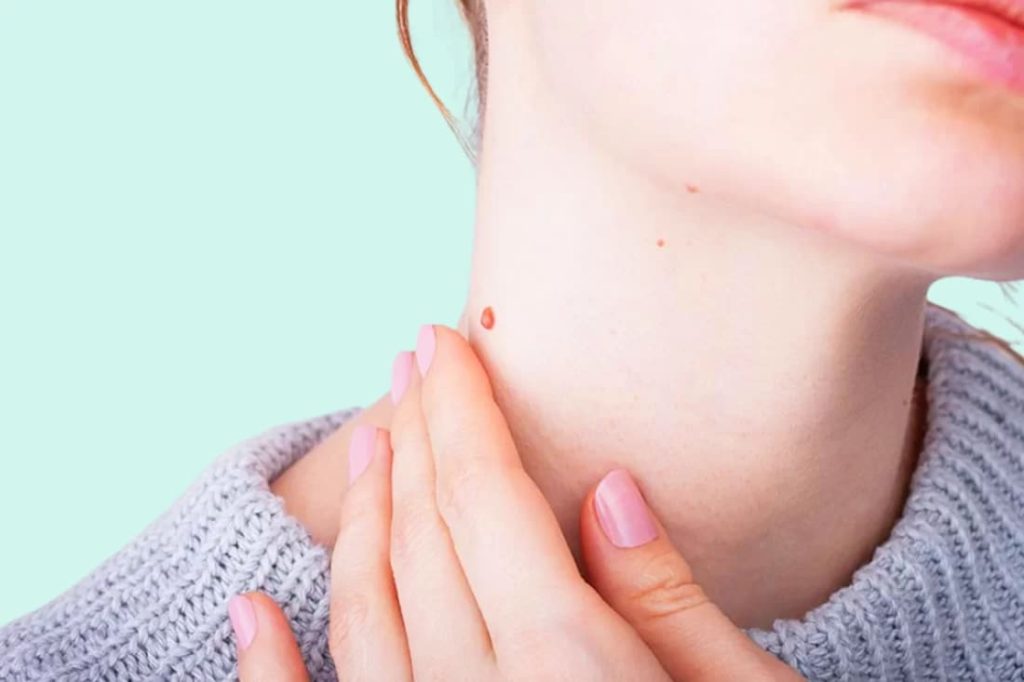
Dermatofibromas and Epidermal
Cysts removal